The ln Command
2015-08-07Reading Time: 5 minutes
The ln command, whose function is to make links, confused me for the longest
time. Here I will give an explanation of how this command works and why I will
find myself using this in the future.
How are files linked to your hard drive?
Before going into what links are, let me briefly take you back to how data is stored. Every file on your computer is linked to a physical place on your hard drive with a particular address, like for your house. This address is unique to your files so that your computer can map your hard drive to the file on your desktop.
Where does ln come in?
The ln command allows you to make “copies” of your data on your computer
without taking up extra room. For example, I have a project where there are
large data files in another directory but I would like to call everything within
my own project folder to make it easier on my scripts. I could copy all of the
data to my own folder but that would make unnecessary duplications of the data.
Here is where ln comes in.
I can create a link file in my own project folder that links to the original data so that it looks like I have the data right in my folder. This link file can exist as one of two types of links: a hard link or a soft/symbolic link.
Hard Links
Simply put, hard links points straight to the hard drive address of the original file. In other words, both files are tied to the same bits and bytes of the file in the hard drive.
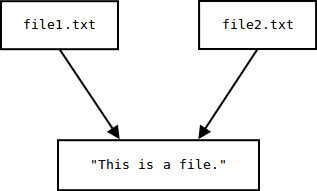
Because the hard link points straight to the hard drive space, changing the name or moving the original file does not affect the hard link.
Soft/Symbolic Links
Soft or symbolic links are slightly different. Instead of pointing to the data on the hard disk, the link points to the original file that you, as a user, can see.
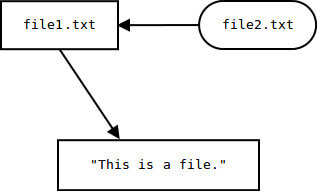
Symbolic links come in handy to point to different directories as they cannot be hard linked to. Another thing to note about soft links are that if you move the original file, the soft link will fail.
More Information
A tutorial will be posted in the future with commands that can be used to make a hard link and a symbolic link but also how it affects how you get to those files.
Image Source: http://www.computerhope.com/unix/uln.htm